Breast Reconstruction Options
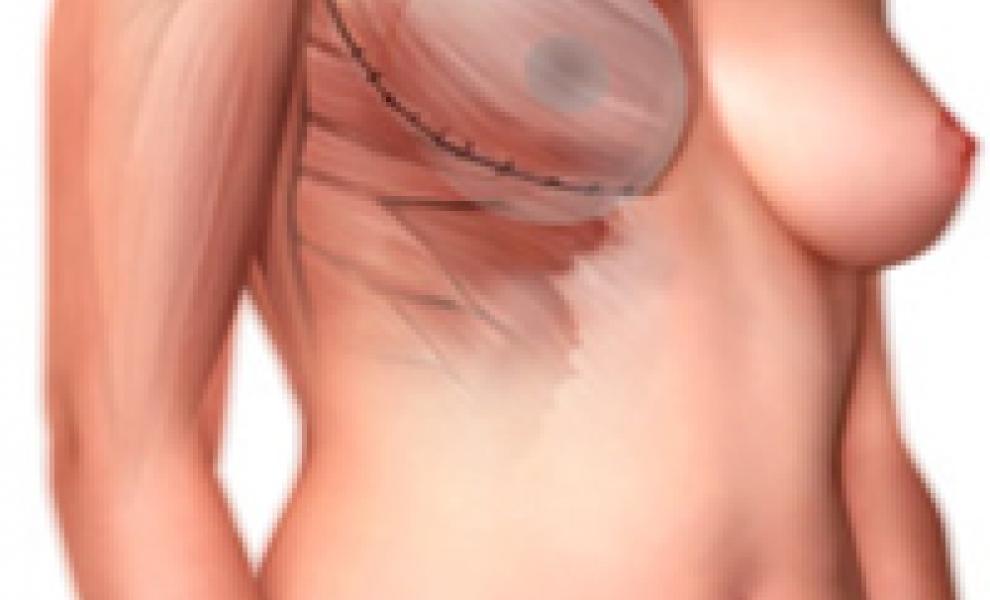
Two stage expander/implant reconstruction: stretches the breast skin and tissue, using a tissue expander, before inserting the final implant.
The first stage involves inserting the expander during a two-hour surgery under general anesthetic. An overnight stay in the hospital is not usually required. Recovery after the first stage is two–four weeks.
The expander is inflated every two weeks over two–three months to make room for the breast implant. Three to six months after the final expansion, the tissue expander is removed and a permanent breast implant is inserted in the second stage. Recovery after the second stage is one to two weeks.
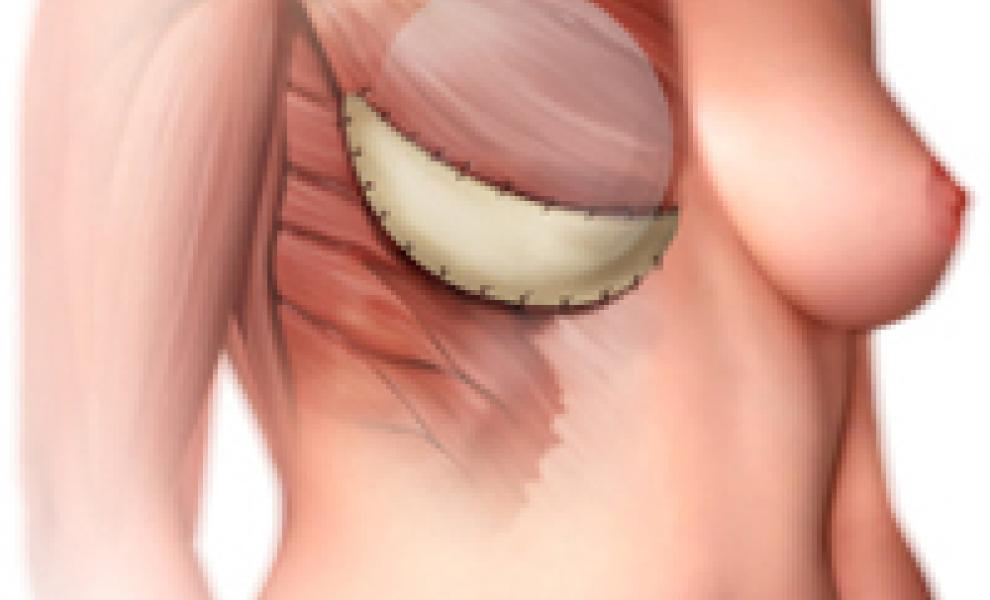
Direct-to-implant reconstruction: is a one-stage implant reconstruction technique with the additional use of tissue replacement.
This surgery lasts two to three hours and is done at the same time as the mastectomy (often a nipple-sparing mastectomy). This procedure does not usually require an overnight stay in hospital. Recovery time is two to four weeks.

Pedicled TRAM flap: This procedure uses the skin and fat of your lower abdomen.
The muscle is divided at its lowermost point in the pelvis and moved into the chest area, where the attached skin and fat are used to create a breast mound.
This is a three- to five-hour surgery, requiring an overnight stay in the hospital. Recovery time is six to eight weeks.
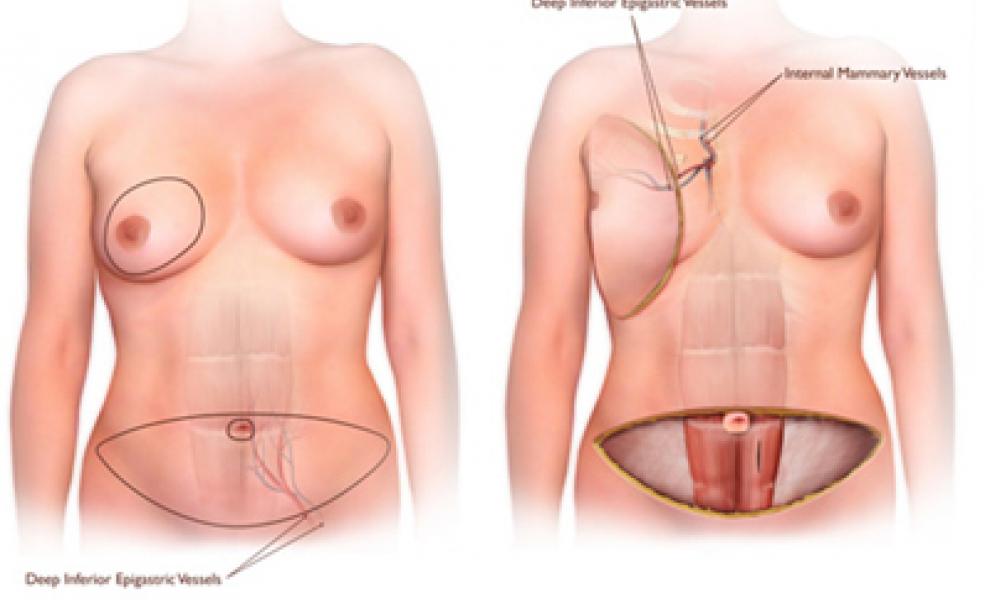
Free Flap (DIEP or other): uses your own abdominal tissue to reconstruct your breast mound. This is one of the “free flap” options for breast reconstruction.
The DIEP flap method detaches the blood supply of the abdominal skin and fat and reconnects it using microsurgical techniques to a new blood supply in the chest area. This is a longer and more complex surgery and requires a hospital stay of about five days.
A free flap program is currently under development at North York General Hospital. Your plastic surgeon will discuss if this option is best for you.

Combined implant and autologous reconstruction: is a method of breast reconstruction that is sometimes used if you have had previous radiation therapy on the breast. Healthy tissue is moved from your back to replace radiated breast skin. An implant may be used to add volume to the breast mound.
The first stage of this procedure involves a three- to five-hour surgery and requires an overnight stay in the hospital. Recovery time is four to six weeks following the first procedure, and 1one to two weeks following the second procedure.
Nipple-areolar reconstruction (nipple reconstruction and tattooing): are optional procedures usually offered at least three months after reconstruction of the breast mound. This may be done in one or two stages under either local or general anesthesia. The most common method of nipple reconstruction involves using skin in the area to create a nipple and tattooing of the areola. Recovery time is short.
